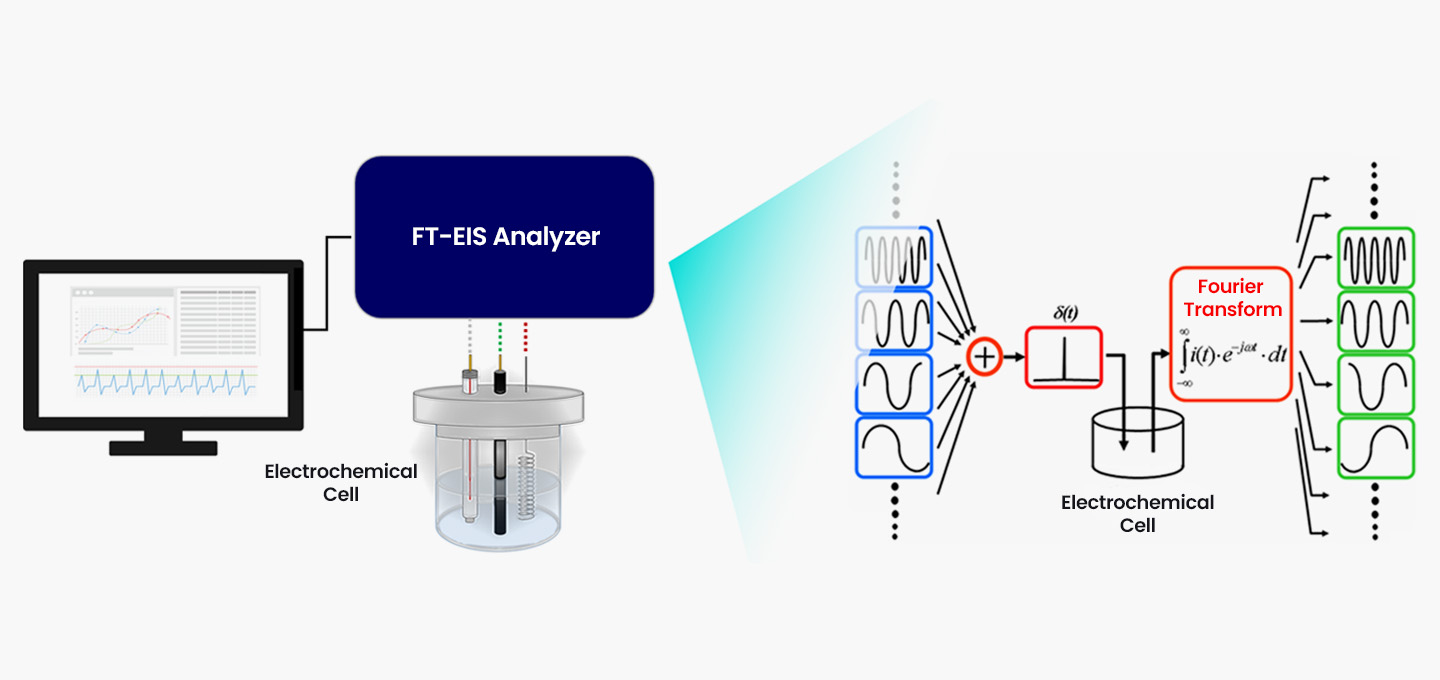
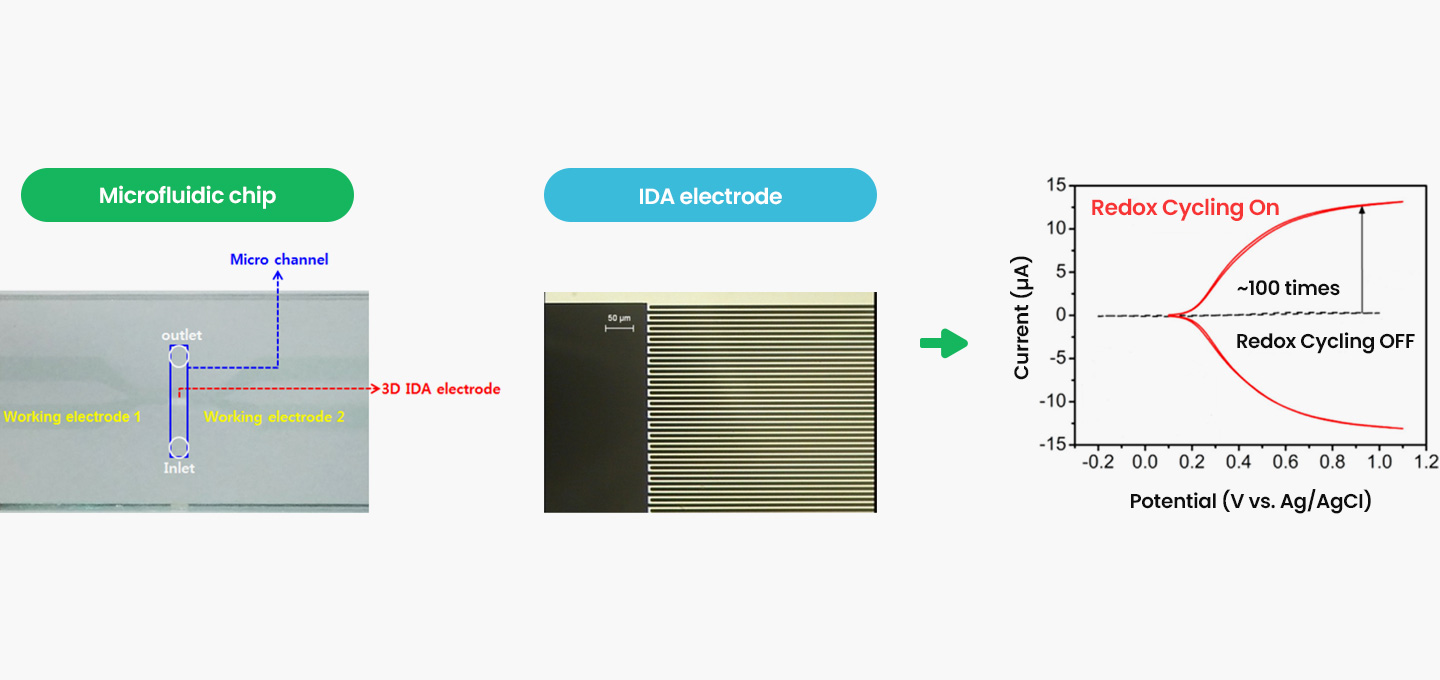
Customized Redox Mediator
Sens. Actuators Rep. 10, 100392 (2025)
Sens. Actuators Rep. 9, 100266 (2025)
Osmium redox complexes play a pivotal role as electron transfer mediators in a wide range of electrochemical systems. Osmium complexes can be precisely tuned by coordinating with various ligands, allowing control over their redox potentials and electrochemical properties to meet specific application needs. This flexibility enables highly efficient and stable electron transfer, making them suitable not only for enzyme-based systems but also for non-enzymatic and electrocatalytic platforms.
These complexes are used across many fields where electron transfer is essential — including medical diagnostics, biofuel cells, electrocatalysis, energy conversion, environmental monitoring, and food safety. Their tunable molecular structures and compatibility with diverse electrode materials and polymer matrices make them highly versatile from lab-scale research to commercial applications.
At CHEMBUD, we specialize in the design, synthesis, and production of osmium-based mediators customized to meet diverse scientific and industrial requirements. Through continued innovation and sustainable material technologies, we strive to be your trusted partner in powering next-generation sensors and energy systems.